What are the Symptoms of Scabies? How Does Scabies Pass? How is scabies transmitted?
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the microscopic parasite Sarcoptes scabiei, manifested by intense itching and skin rashes. This parasite settles on the surface of the skin, opens small tunnels and lays its eggs. The body’s immune system reacts to this situation, and an itching sensation appears. This itching, which increases especially at night, is one of the most obvious symptoms of the disease.
What is Scabies?
Scabies is a contagious skin disease caused by a microscopic parasite called Sarcoptes scabiei, manifested by intense itching and rashes on the skin. This parasite settles on the surface of the skin, digging tunnels and laying its eggs. The main cause of itching is not the parasite itself, but the reaction of the body’s immune system to this parasite.
Scabies is a common disease around the world and can affect anyone, regardless of hygiene conditions. Because it is easily transmitted, especially through close contact, it can spread rapidly between individuals living in the same household.
What Are the Symptoms of Scabies?
Symptoms of scabies usually occur due to an allergic reaction and irritation caused by mites.
- Intense itching
- Redness and Skin Rash
- Tunnel Traces
- Wounds on the skin
- Condensation in certain parts of the body
- Crusted Scabies (Norway Scabies)
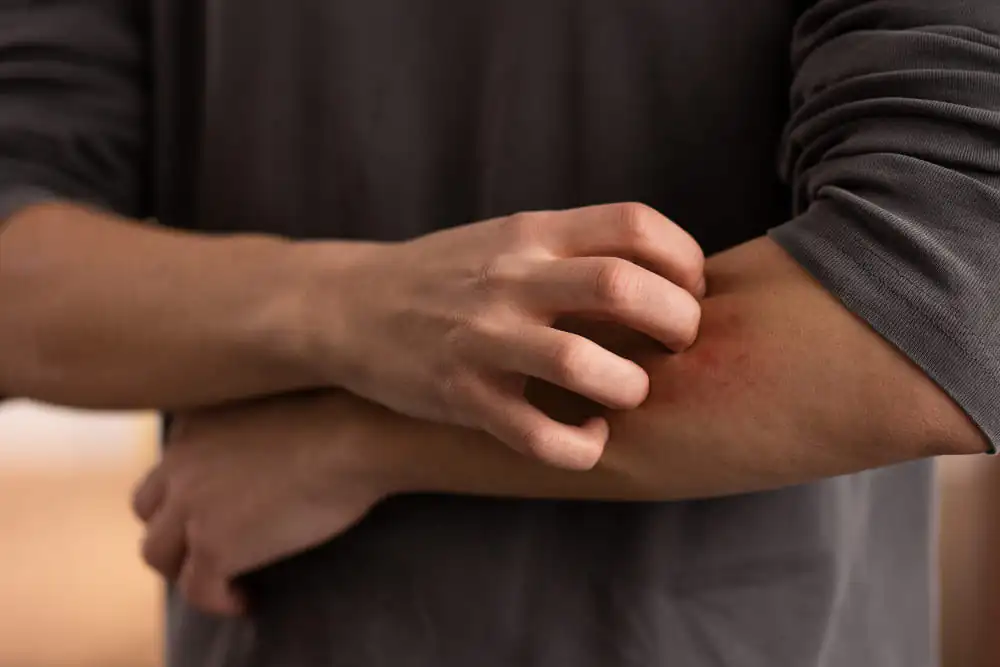
1. Intense Itching
The most obvious symptom is itching, which usually becomes more severe at night. This is associated with the activation of mites under the skin.
2. Redness and Skin Rash
- Due to the tunnels dug by mites, red dots, blisters and rashes form on the skin.
- The rash is usually small blisters or pimple-like in appearance.
3. Tunnel Traces
The tunnels that the mites dig under the skin can be seen as thin, streak-shaped gray-white scars. These scars are usually 5-15 mm long.
4. Wounds on the skin
Open wounds may form on the skin due to severe scratching. If these wounds become infected, bacterial infections can develop.
- Between the fingers
- Wrists
- Elbows
- Armpits
- Waist circumference
- Nipple circumference (in women)
- Genital area (in men)
- In children, the head, face, palms and soles of the feet can also be affected.
6. Crusted Scabies (Norway Scabies)
In people with weakened immune systems, thick, gray-white crusts may form on the skin. This type of scabies has a heavier course and carries a heavy mite load.
How Is Scabies Transmitted?
Scabies is usually transmitted through direct skin contact. The parasite requires close contact for several minutes to pass from one person to another. In addition, shared items (bedding, towels, clothes) can also be a source of transmission. How scabies is transmitted:
- Direct Skin Contact: Prolonged and close contact is the main route of transmission of scabies. For example, sleeping in the same bed or holding hands is contagious.
- Common Items: The parasite can also be transmitted through bedspreads, pillows, or clothing used by the infected person. However, this route is less common than direct contact.
- Crowded Environments: Scabies outbreaks are more common in crowded and close contact places such as dormitories, nursing homes, and prisons.
Since the parasite cannot live outside the skin for a long time, transmission usually requires direct contact with an infected individual.
What Causes Scabies?
The main cause of scabies is the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei. This parasite settles on the surface of the skin, where it tunnels and lays its eggs. This action of the parasite activates the body’s immune system and leads to intense itching.
- Close contact with an infected person
- Even if there is no lack of hygiene, being in crowded and closed environments for a long time
- Having a weak immune system (for example, the elderly or individuals with chronic diseases)
Scabies Disease Treatment
Treatment for scabies is highly effective, and most people recover within a few weeks with the right treatment. The goal of treatment is to completely eliminate the parasite and its eggs.
- Topical Medications: The most commonly used drugs in the treatment of scabies are antiparasitic products in the form of creams or lotions. These drugs are applied to the entire body (except the face and head) and are usually left on the skin for 8-12 hours.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases or in cases where there is no response to topical treatment, the doctor may prescribe antiparasitic drugs that are taken by mouth.
- Anti-Itch Medications: Antihistamines or corticosteroids may be recommended to relieve itching and allergic reactions.
- Whole Family Treatment: Because scabies is highly contagious, it is important that everyone living in the same household is treated simultaneously.
Things to consider during the treatment of scabies:
- High-temperature washing of all clothes, sheets and towels
- Keeping unusable items in airtight bags for a few days
- It should be remembered that itching may persist for some time after treatment; This is the response process of the immune system and does not mean that the disease is continuing.
Scabies Disease Frequently Asked Questions
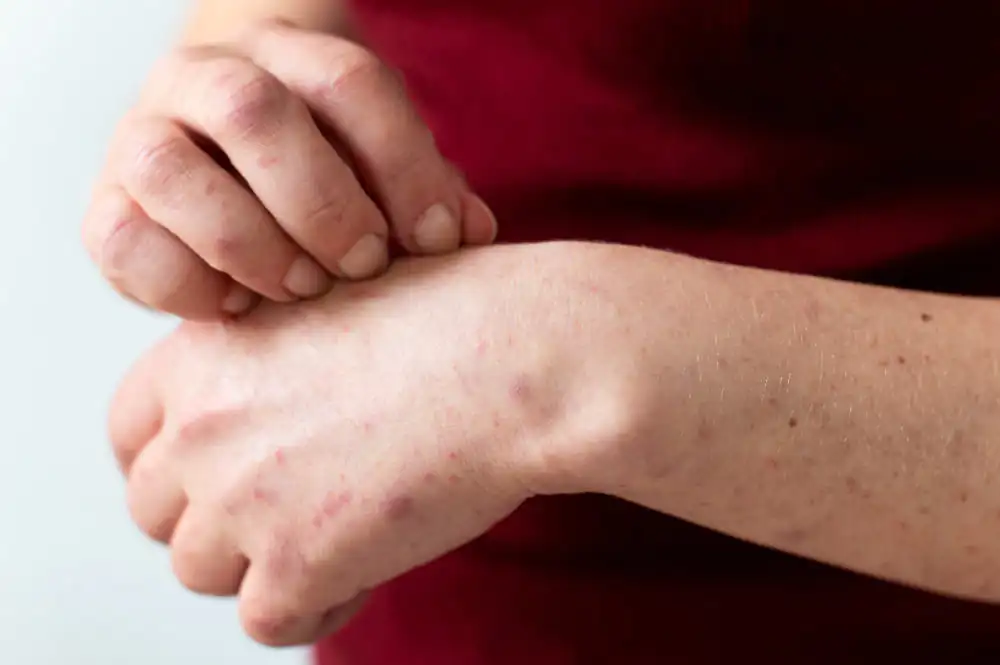
Symptoms of scabies on the hand
Hands are one of the areas where symptoms of scabies are most common. The parasite forms tunnels between the fingers and around the wrist, where it causes itching and skin rashes. Symptoms of scabies can be seen in the form of fine lines, small water-filled blisters, or redness on the hands.
Symptoms of the onset of scabies
The first signs of scabies appear 2-6 weeks after infection. Among the symptoms of scabies in man, the most common is intense itching, which increases at night. During this period, redness, rashes and thin tunnel scars caused by parasites can be observed on the skin.
How Many Days Does Scabies Go Away?
Once scabies treatment begins, the parasites usually die within 1-2 days. However, itching and rashes on the skin may persist for several more weeks due to the immune system’s response. If the treatment is carried out correctly, the disease will be completely cured in 2-4 weeks.




